Sickle cell Disease is a group of inherited red blood cells disorders. Red blood cells contain Haemoglobin (Hb), a protein that carries oxygen. Healthy red blood cells are round, and they move through small blood vessels to carry oxygen to all parts of the body. In someone who has Sickle Cell Disease, the Hb is abnormal, which causes the red blood cells to become hard and sticky and look like a C-shaped farm tool called “Sickle”. The sickle cells die early, which causes a constant shortage of red blood cells. Also, when they travel through small blood vessels, they get stuck and clog the blood flow. This can cause pain and other serious complications.
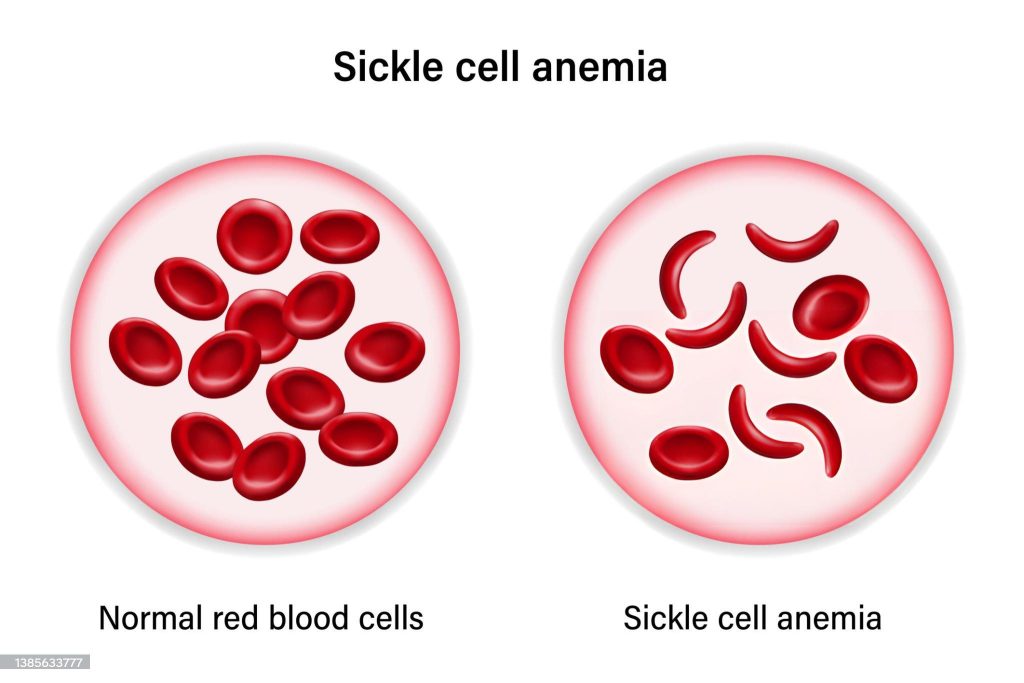
Sickle Cell Anaemia (SCA) is the most common autosomal recessive disorder and the most common cause of hemolytic Anemia in African Americans. Approximately 8% of African Americans carry the gene (sickle cell trait),with 1 in 625 affected by the disease.
Types of Sickle Cell Disease
There are several types of SCD depending on the genes inherited from their parents.
- Hbss: People with this form of SCD inherit 2 genes, one from each parent that codes for hemoglobin ”S”, an abnormal form of Hb that causes the red blood cells to become rigid and sickle shaped .This is commonly called Sickle Cell Anaemia and is the most severe form of the disease.
- Hbsc: This group of people inherit a Hb “S” gene from one parent and a gene for a different type of abnormal Hb called C from other parent .This is a milder form of SCD.
- Hbs beta thalassemia: People with this form of SCD inherit a Hb “S’ gene from one parent and a gene for beta thalassemia, another type of Hb abnormality from the other parent.
There are 2 types of Hbs beta thalassemia ; Hbs beta 0 ( severe form) and Hbs beta+(milder form)
Factors that enhance Sickling include:
- Increased Oxygen tension.
- Increased WBC
- Fever
- Presence of bacteria.
Clinical Features of SCA include
- Pallor/Anemia.
- Jaundice.
- Hepatosplenomegaly.
- Dctilitis.
- Hand-foot syndrome
Complications of SCD
- Pain crises: Due to consequence of microvascular occlusion of bones by sickled cells.
- Infections: Patients with SCD are at greater risk of infections.
- Acute Chest Syndrome: This is a Vaso-Occlusive crises within the lungs and it’s associated with chest pain, fever, infection etc.
- Priapism: Sustained painful penile erection due to obstruction of venous outflow from the Copora Cavernosa. Its a risk for partial or complete impotence.
- Cardiovascular Accidents: results from partial or complete occlusion of major cerebral vessels. May present with Convulsions, Coma, drowsiness, hemiplegia and stroke.
- Aplastic Crises: occurs secondary to Viral Suppression of red blood cells precursors especially by parvovirus B19. It occurs because of the very short half life of sickled red blood cells.
Management of Sickle Cell Disease
- Analgesia
- Red Cell Exchange
- Hydration
- Oxgenation
- Keep Warm
Can Sickle Cell Disease be Cured?
- Bone Marrow Transplantation: This has potential for cure and preserved for patients with severe clinical course.
And According to an article in NHS UK website:
Stem cell or bone marrow transplants are the only cure for sickle cell disease, but they’re not done very often because of the significant risks involved. Stem cells are special cells produced by bone marrow, a spongy tissue found in the centre of some bones. They can turn into different types of blood cells. For a stem cell transplant, stem cells from a healthy donor are given through a drip into a vein. These cells then start to produce healthy red blood cells to replace the sickle cells. A stem cell transplant is an intensive treatment that carries a number of risks. The main risk is graft versus host disease, a life-threatening problem where the transplanted cells start to attack the other cells in your body. Stem cell transplants are generally only considered in children with sickle cell disease who have severe symptoms that have not responded to other treatments, when the long-term benefits of a transplant are thought to outweigh the possible risks.
- Prevention: Prevention is better than cure!!
Prevention of Sickle Cell Disease
- Public awareness/Education
- Genetic Counseling: Premarital Counseling and screening
- Prenatal Diagnosis: Selective abortion
- Routine neonatal Screening: early diagnosis and follow up.
Read more via NHS.uk





4 Comments
Educative Content. Thanks for sharing
Thank you so much.
This is very educative and interesting.
This is very educative and interesting i would to apart of this